By Peter A. McCullough, MD, MPH
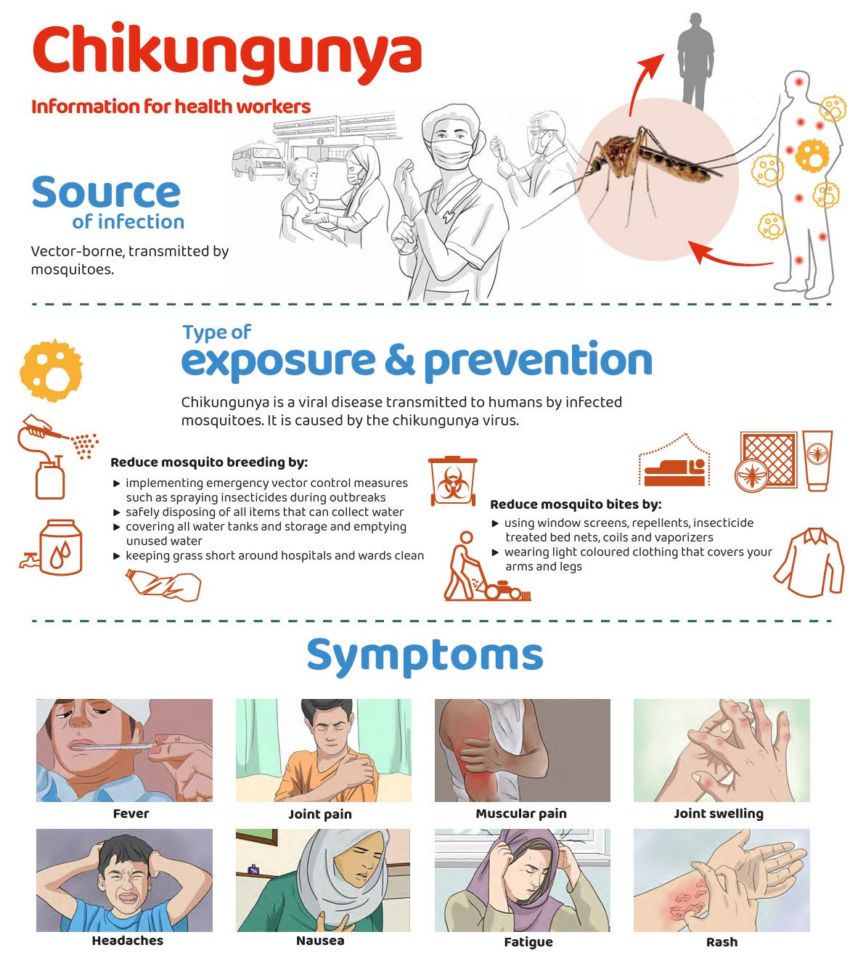
Chikungunya disease is a common illness caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), a virus transmitted to humans by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, particularly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. The name itself, derived from the Makonde language of Tanzania where the virus was first identified in 1952, means “that which bends up”, referring to the stooped posture often adopted by those suffering from the disease’s severe joint pain.
Recent news stories on the illness has prompted travellers to explore current available drugs that could be entertained for off-label use.
Niclosamide is a medication primarily used to treat infections caused by tapeworms, such as broad or fish tapeworms, dwarf tapeworms, and beef tapeworms. It’s an anthelmintic, a class of drugs designed to eliminate parasitic worms from the body.
Niclosamide functions by interfering with the tapeworm’s metabolism, particularly by disrupting its ability to absorb glucose and produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through oxidative phosphorylation. This essentially starves the tapeworm of energy, leading to its demise. The dead worms are then passed out of the body through stool.
Nitazoxanide (often sold under the brand name Alinia) is a broad-spectrum anti-infective medication used primarily to treat diarrhea caused by certain parasitic infections. It is particularly effective against infections caused by the protozoa Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium parvum.
Click this link for the original source of this article.
Author: Peter A. McCullough, MD, MPH
This content is courtesy of, and owned and copyrighted by, https://petermcculloughmd.substack.com and its author. This content is made available by use of the public RSS feed offered by the host site and is used for educational purposes only. If you are the author or represent the host site and would like this content removed now and in the future, please contact USSANews.com using the email address in the Contact page found in the website menu.