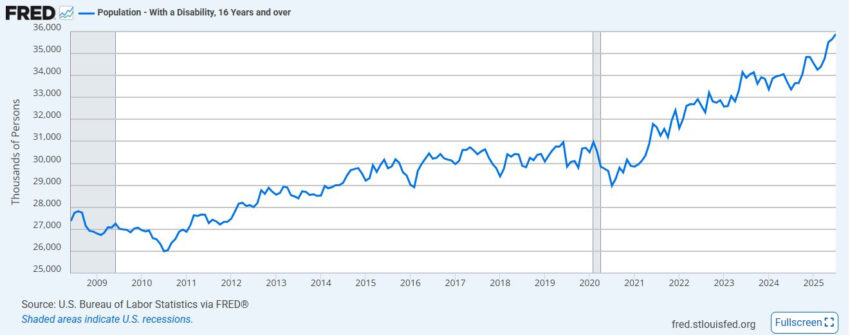
Before we get to the horrifying data that once again proves that these Modified mRNA slow kill bioweapon “vaccines” are genetically modifying future generations, even if they are not directly injected with these EUA poisons, let us briefly review a grim statistic for those demographics that did get these democide shots:
As predicted by this Substack years ago, this disability trend, directly in line with VAIDS symptoms that are increasingly expressing themselves across all age groups, even ones that historically never came down with diseases such as (turbo) cancer, will only get worse.
And now let us review the gene altering implications of these murderous “vaccines” in the newly born and unborn alike…
This follow-up to our earlier report, Houston, We Have a Problem, identifies a new and deeply concerning signal: excess infant and child mortality in those who neither contracted Covid-19 nor received the vaccine themselves, but whose parents bore prior mRNA exposure. The evidence points to two neglected risks—teratogenic effects passed in utero and transgenerational epigenetic effects transmitted through germline biology—together forming a warning of historic consequence for generations yet unborn.
We again invoke the Apollo 13 crew’s now-immortal phrase, “Houston, we have a problem,” as the title-thematic of this article—offered as a direct continuation of our earlier blockbuster report, Houston, We Have a Problem. That first analysis marked the earliest significant identification of morbidity and mortality impacts associated with the Covid-19 mRNA vaccine. It stood as a “shot heard around the world,” revealing excess non-Covid natural-cause mortality across multiple ICD-coded categories documented within the National Vital Statistics System (NVSS). Much as thalidomide once forced medicine to reckon with teratogenic risk, these findings underscored the ethical necessity of considering systemic, population-wide harms that may only emerge through rigorous epidemiological tracking.
Now, a parallel recognition confronts us—not within our own generation, whose members bore the primary exposure to the vaccine, but rather within the realm of our heritable biology. The detectable signal has shifted downstream, appearing in our youngest children: those who neither contracted Covid-19 nor ever received an mRNA injection, yet who manifest the biological consequences of their parents’ exposure (In this study, mRNA-1273 intramuscularly given to pregnant mice rapidly circulated in maternal blood and crossed the placenta within 1 h to spread in the fetal circulation.1)
This emergent pattern suggests not merely an immediate pharmacological effect, but the unsettling possibility of developmental and epigenetic inheritance—echoes of intervention carried into lives that never consented to it.
The mRNA vaccination program—rushed into deployment under an imperious, treatment-embargoing emergency use authorization (EUA)—carries with it two overlooked categories of risk, which this article addresses directly:2
-
Teratogenic potential (adjective phrase) — The possibility of inducing congenital morbidity or mortality in those exposed in utero. Refers to any agent or factor capable of causing malformations, developmental abnormalities, or functional deficits in an embryo or fetus during pregnancy. In the context of mRNA vaccination, concern centers on the passage of synthetic mRNA instructions and their biological consequences through the placental barrier, where such exposures may be encoded into embryonic and fetal development.
-
Transgenerational / Epigenetic potential (noun phrase) — The possibility of producing biological changes in health, development, or disease risk in generations never directly exposed to the original agent. Unlike genetic mutations, these effects arise through heritable epigenetic mechanisms—such as DNA methylation, histone modification, or non-coding RNA—that alter gene expression across generations. In the context of mRNA vaccination, concern centers on the passage of synthetic mRNA instructions and their biological consequences through the female ovary–egg–zygote cycle, where exposures affecting germline cells may be encoded into embryonic development and transmitted to descendants.3
What follows is an examination of the data signals emerging from national vital statistics and mortality datasets. Our approach draws on methods from both systems science and epidemiology, relying heavily on a technique central to our signal detection: Deviation from Trend analysis (DFT Charting). This method allows us to isolate meaningful departures from long-established baselines, revealing anomalies that conventional year-over-year comparisons often obscure.
Rather than relying on raw mortality counts—which naturally fluctuate with seasonality, demographics, and shifts in diagnostic practice—we focus on whether mortality curves themselves exhibit inflections. An inflection is a statistically significant and sustained change in a trajectory’s slope, rate, or variability, occurring in temporal association with a specific intervention or event. To strengthen this analysis, we will cross-reference findings with the CDC/NCHS’s own published data (Chart 1) and confirm them through raw mortality charting as well (Chart 4).
By concentrating on the points where long-established declines in infant and child mortality were broken, and by measuring how sharply the new trajectories deviate from their expected baselines, we can detect signals that would otherwise be lost in statistical noise.
The data used in this study are not projections or speculative estimates, but are drawn directly from the CDC WONDER / NCHS Multiple Cause of Death database, which records every U.S. death certificate. For this analysis, we isolate mortality in children ages 0–4, exclude deaths formally attributed to Covid-19 (ICD-10 U07.1), and compare the observed outcomes against 30-year-stable pre-2020 legacy benchmarks (see Chart 1).
This approach enables us to separate ordinary year-to-year fluctuations from extraordinary, persistent departures—shifts that align temporally with the introduction of mRNA vaccination among childbearing populations.
Teratogenic Potential
Chart 1: Infant, Neonatal, and Postneonatal Mortality (1995–2023)
This chart, from the National Vital Statistics Reports Volume 74, Number 7 June 10, 2025 Infant Mortality in the United States, tracks infant deaths per 1,000 live births across nearly three decades. Until 2021, mortality rates trended steadily downward, reflecting advances in maternal care, neonatal medicine, and socioeconomic improvements. However, the period commencing with and following 2021 shows a break in that 30-year consistency: instead of declining further, neonatal and postneonatal mortality abruptly change from a legacy trend, to an entirely novel one.
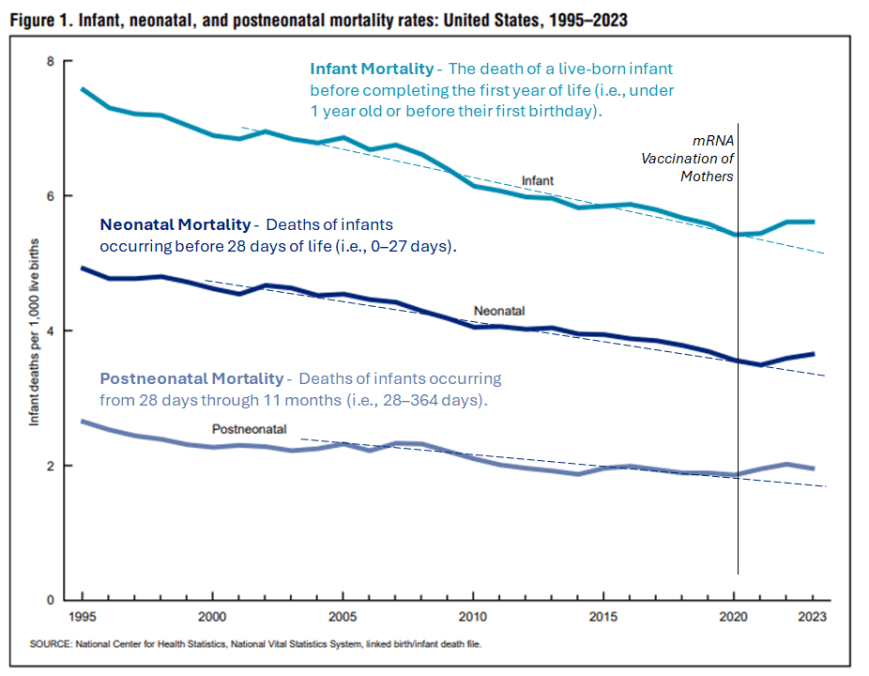
The vertical marker identifies the introduction of mRNA vaccination among, not only expectant mothers, but future mothers as well, during the February to June 2021 timeframe. The disruption in trajectory aligns temporally with this intervention, suggesting possible teratogenic influences. While temporal association is not proof of mechanism, the reversal of decades-long progress warrants critical examination.
Transgenerational / Epigenetic Potential (Vaccinial Generation)
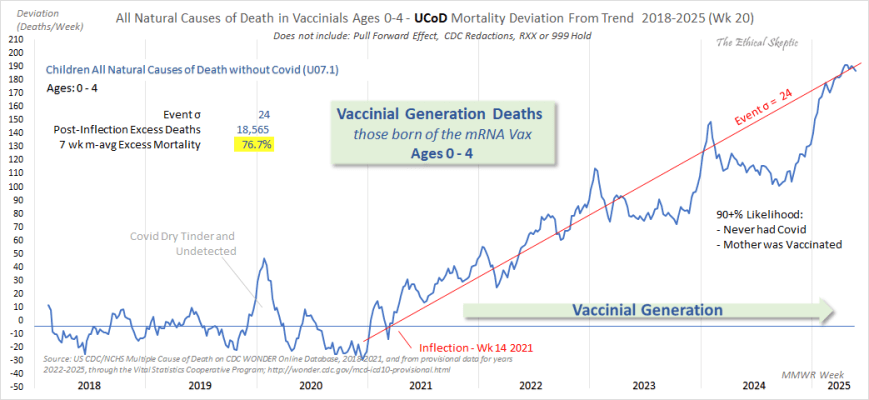
Chart 2 & 3: All Natural Causes of Death in Vaccinal Generation (Ages 0–4)
Here, mortality deviations from the expected baseline are charted for children born after maternal and maternal candidate vaccination. The persistence of this deviation well into a period when more than 90% of the U.S. population had ceased further mRNA vaccination suggests that the effect is not confined to exposures during pregnancy. Rather, it points to an impact carried forward from prior vaccination in women who later became pregnant—indicating that the risk extends beyond gestational exposure to include those merely planning to conceive in the future.
The data, sourced from CDC WONDER, exclude all deaths directly attributed to Covid-19. The brief spike visible in late 2019 and early 2020 reflects a dry-tinder effect—mortality rising in populations already vulnerable—occurring during a period when the virus was either not yet formally detected, or not yet recognized as having reached U.S. shores.
Methods and Data Considerations
The key signal: an inflection point in Week 14 of 2021, immediately following mass vaccination of childbearing-age adults. From this point onward, all-cause mortality among 0–4 year-olds climbs persistently, reaching a deviation event size of σ = 24, or 18,565 excess deaths (76.7% above baseline). The rise is not random noise—it is systemic, compounding across multiple morbidity categories. Of significant and ominous merit, when conducting a differential-summary query by time period from the Wonder data, these ICD group dynamics mirror those same dynamics as to the impact of the mRNA vaccine in adult primary recipients:
Excess Mortality Broad ICD Grouping (Parallel Vaccinated Adult Mortality Rises):
-
Renal function related (+135%)
-
Meningitis related (+112%)
-
Virus and septicaemia susceptibility (+90%)
-
Liver/digestive disorders (+82%)
-
Respiratory related (+54%)
-
Congenital malformations (+51%)
-
Cardiopulmonary disorders (+38%)
-
Nervous/epileptic related (+37%)
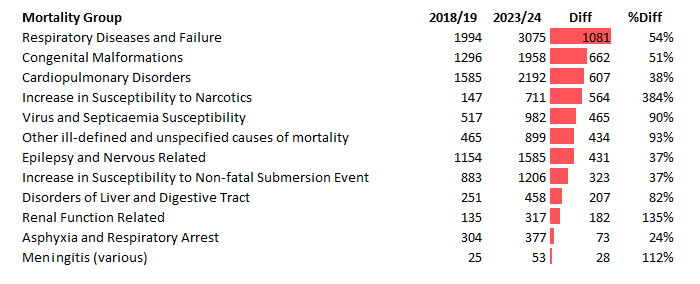
These ICD groupings account for 7,600 deaths—41% of the excess mortality identified in Chart 2 above. The impact on the yet-to-be-born is therefore not narrow, but pervasive, extending across multiple physiological domains. Such a pattern is more consistent with heritable or gestationally imprinted vulnerabilities than with isolated anomalies, pointing toward epigenetic disturbance or germline modification. This is not simply a teratogenic effect on a single child, but a generational echo reverberating across thousands.
The fact that this data parallels with elevated mortalities in mRNA vaccinated adults is particularly alarming.
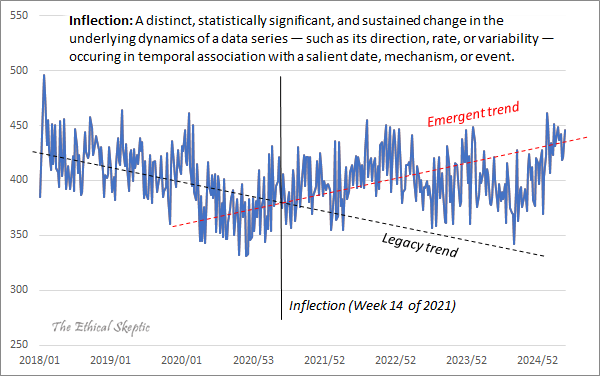
Chart 4: What is an Inflection (DFT Chart)?
An inflection is a distinct (a discrete contribution that is abrupt, constrained, pronounced, and definitive), statistically significant, and sustained change in the underlying dynamics of a data series — such as its direction, rate, or variability — occuring in temporal association with a salient date, mechanism, or event. Legacy mortality trends had been in long decline; post-2021, the slope then suddenly reversed.
Deviation-from-Trend (DFT) analysis strips away seasonal fluctuations and background variation to reveal the underlying signal. This method is widely applied in fields characterized by strong seasonality—such as consumer goods forecasting, where it is used to detect sudden demand shifts hidden beneath predictable holiday or back-to-school cycles—and is equally valuable in mortality analysis. Here, it exposes the onset of the “vaccinal generation” mortality surge as a clear break from prior patterns. Without DFT, such anomalies can be obscured by averaging, linear regression, or annualization—techniques that smooth away signal and invite convenient dismissal as “random noise,” a tactic too often employed by agenda-driven defenders of the pharmaceutical narrative.
Conclusion
As we have observed in prior analyses of systemic injury, such morbidity and mortality events rarely remain confined to “rare occurrences”; over time, they manifest across the entire recipient population, though to varying degrees of severity. For example, asbestos exposure did not produce mesothelioma in every worker, but no exposure was without consequence—some suffered respiratory decline, others chronic inflammation, and still others terminal disease.
Invulnerability Bias or ‘Red Shirt Fallacy’
When a person incorrectly assumes that injury can only happen to a constrained group of persons (those wearing Star Trek’s proverbial ‘red shirts’) and not to them.
In the same way, the evidence presented here raises two problems of historic consequence:
Teratogenicity — Mortality curves in infants, neonates, and children—none of whom were exposed to either Covid-19 or its mRNA vaccine—shifted upward after decades of steady decline, coinciding with the mass introduction of mRNA vaccination to both expectant and future mothers.
Intergenerational Effect — Children born after the rollout are experiencing sustained excess mortality across multiple physiological domains, a pattern consistent with systemic biological disruption. Alarmingly, these effects mirror the very disruptions documented in adults who were direct recipients of the Covid-19 mRNA vaccine.
It should be noted that TES was the first analyst to previously and successfully identify both Excess Non-Covid Natural Cause Mortality and Excess Cancer Mortality signals using this same analytical framework—findings now broadly acknowledged in mainstream datasets. This track record underscores that the method employed here is neither speculative nor dismissible, but a proven approach to signal detection.
These signals demand immediate, transparent, and unflinching investigation. To dismiss them is not only to deny the data but to gamble recklessly with the health of the living and the yet-to-be-born alike.
Do NOT comply.
Click this link for the original source of this article.
Author: 2nd Smartest Guy in the World
This content is courtesy of, and owned and copyrighted by, https://2ndsmartestguyintheworld.substack.com and its author. This content is made available by use of the public RSS feed offered by the host site and is used for educational purposes only. If you are the author or represent the host site and would like this content removed now and in the future, please contact USSANews.com using the email address in the Contact page found in the website menu.